Unkategorisiert
Spirulina in short portrait
The microalgae spirulina
The blue-green microalgae Spirulina – also called “Arthrospira platensis” – is one of the oldest organisms on our planet. Due to its properties of interest for healthy nutrition, spirulina is often called Superfood referred to. Spirulina contains various antioxidants such as carotenoids (mix of carotene and xanthophyll), green chlorophyll and the blue pigment phycocyanin – this is found only in Spirulina algae. In addition, The Purity Brand’s organic Spirulina serves as a high protein food and natural source of iron. The safety of spirulina as a food has been established by toxicological studies demonstrated.
This is what the World Health Organization (WHO) says about Spirulina
The microalgae Spirulina has long been known for its high content of proteins and essential amino acids as well as carotenoids (5 to 20 mg/gram Spirulina), minerals (e.g. magnesium 1 to 5 mg/gram Spirulina), essential fatty acids and e.g. polysaccharides (1-4). For this reason, spirulina is often used as a functional food whose consumption benefits human health (5). The WHO (World Health Organization) pointed out that Spirulina is one of the most important superfoods on earth and gave Spirulina the title “Food of the Future”. NASA uses spirulina for spaceflight because a small amount of spirulina can provide a wide range of nutrients (6, 7).
- Sorrenti V. et al. Spirulina Microalgae and Brain Health: A Scoping Review of experimental and clinical Evidence. Mar Drugs 2021, 19: 293
- Babadzhanov, A. et al. Chemical Composition of Spirulina platensis cultivated in Uzbekistan. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2004, 40, 276-279
- Vonshak, A. Spirulina Platensis Arthrospira: Physiology, Cell-Biology and Biotechnology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997.
- Liestianty, D. et al. Nutritional analysis of spirulina sp to promote as superfood candidate. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019
- Khan, Z.; Bhadouria, P.; Bisen, P. Nutritional and therapeutic potential of Spirulina. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2005, 6, 373-379.
- Karkos, P. et al. Spirulina in clinical practice: evidence-based human applications. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2011
- Mahasin, G.T., Robert, D.M. Characterization of Spirulina Biomass for CELSS Diet Potential NASA Contractor 1988.
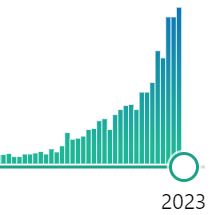
The food market and the development of “new” foods are on the move worldwide, as seen, for example, in the development of vegan burgers as an alternative to animal foods and the trend to use insects as a protein source in foods. In the search for the “foods of the future”, vital substance-rich plant foods such as spirulina are highly interesting, and interest in spirulina is growing visibly, as the adjacent graphic to Spirulina publications from the National Library of Medicine shows!